User manual
Getting Started
What is FITS?
The File Information Tool Set (FITS) identifies, validates and extracts technical metadata for a wide range of file formats. It acts as a wrapper, invoking and managing the output from several other open source tools. Output from these tools are converted into a common format, compared to one another and consolidated into a single XML output file. FITS is written in Java and is compatible with Java 1.8 or higher.
The external tools currently used are:
- Apache Tika
- Jhove
- MediaInfo
- Exiftool
- National Library of New Zealand Metadata Extractor
- DROID
- FFIdent
- File Utility (windows)
Why use FITS?
Preservationists and digital curators who are concerned with long-term access and use of digital files might extract technical metadata from digital files to troubleshoot problems and to create a record of the file’s properties. A number of tools can reliably extract technical metadata, but the File Information Tool Set combines these tools and compares the results of their output; this saves time and effort.
Installing FITS
See our Quick Start guide to get started. Then, come back here to learn more about using FITS.
Using FITS
How FITS processes
FITS works in different stages as shown in the image below.
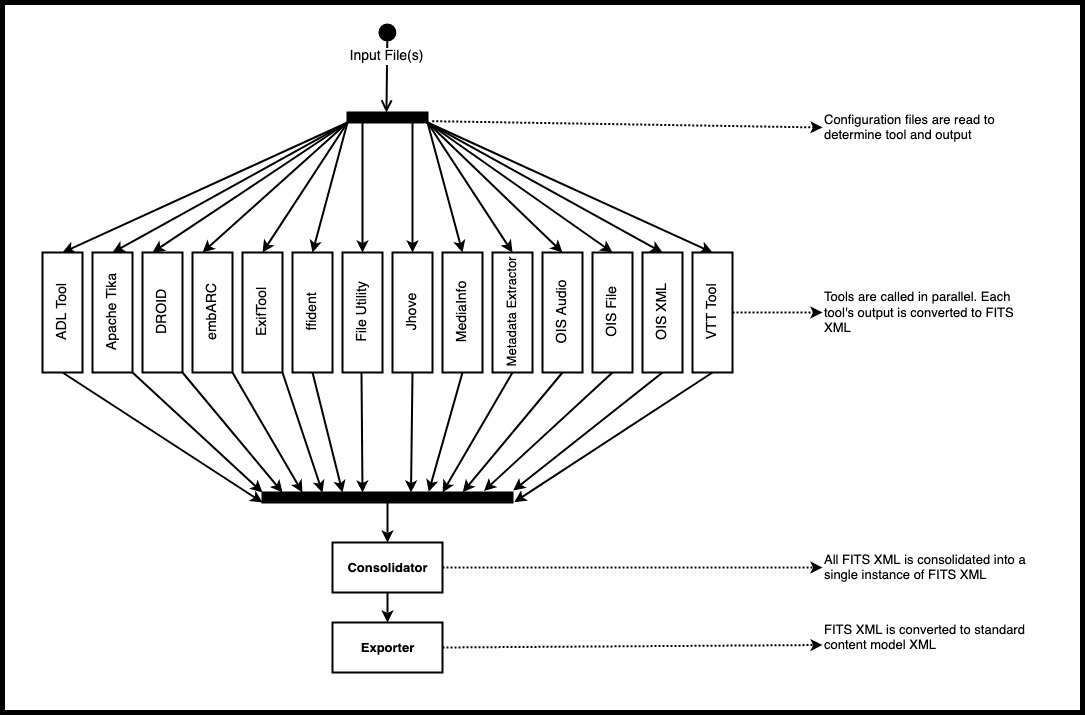
The steps are described in more detail here.
- First the configuration files are read. This determines which tools are called and can affect the output.
- Each tool (JHOVE etc.) is called in parallel to process the file or directory of files (depending on the option used). Each tool’s native output is converted to FITS XML.
- All of the FITS XML is consolidated into a single instance of FITS XML.
- The FITS XML is converted to standard XML (e.g. MIX) (if this option was requested for example by using the -x parameter on the command line).
For a more technical description of FITS processing - see the Developer Manual.
Reading the output
Output format
The output format of FITS is controlled by the options used when executing FITS, how FITS is configured and the genre of the format.
The format of the output will include one or more of the following:
FITS XML
- This is the default output described in detail here
Standardized Metadata
- This is format genre-specific technical metadata in community-standard XML schemas
- When using the command-line, use the -x parameter (to just get the output in standard metadata), or -xc (to get FITS XML in addition to standard metadata)
- The specific XML schema used is determined by the format genre - for more information see the standard metadata schemas
Raw output
- This is the pre-normalized output of each tool run against the file
- This is specified by the display-tool-output configuration property in the fits.xml configuration file
Output destination
Terminal
- This is the default unless an output file is specified
File
- When using the command-line, use the -o
parameter - When using the Java API, use the FitsOutput.saveToDisk method
References
Command-line options
When you run FITS on the command-line, the following options are available:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -h | Prints a help message to the screen. |
| -i | Indicates that a file or directory to process will follow. (required) |
| -o | Directs the FITS output to a file (if -i is a directory) rather than console. (optional) |
| -r | Causes FITS to recursively process all files when the input is a directory. All output files are placed in the same directory as configured in -o unless -n is set. (optional) |
| -n | When -r is set and -i is a directory, output files are placed in nested directories in the same way the input directories are nested. (optional) |
| -v | Outputs tool version information. |
| -x | Transforms the FITS output into standard XML schemas. (Only standard schema metadata is output.) |
| -xc | Outputs the FITS output plus the FITS output transformed into standard XML schemas. |
| -f | Path to an alternate fits.xml configuration file rather than using the default within FITS. (optional) |
Many of the options can be used together. For example:
.\fits.bat -i myFileToProcess.pdf -o theOutput.txt
When processing multiple files contained in a single directory whose output goes to another directory while using an alternate FITS configuration file:
./fits.sh -i /input-files-directory -o /output-directory -xc -f /alternate-fits-config/fits.xml
Data dictionary
FITS converts the raw output of each wrapped tool to a structure called FITS XML. FITS XML schema is maintained by Harvard Library.
The FITS Schema also includes additional top-level elements: technicalMetadata, toolOutputType, and statistics.
1.0 identification
| Semantic unit | 1.0 identification |
| Semantic components | 1.1identity 1.2tool 1.3version 1.4externalIdentifier |
| Definition | This section contains the file format in one or more identity blocks. |
| Rationale | Each file processed with FITS should have a unique format to support use and rendering. |
| Data constraint | Container |
| Repeatability | Not repeatable |
| Obligation | Automatic |
| Usage notes | If all the tools that processed the file and could identify it came up with the same format, there will only be one identity block. If there were tools that processed the file that came up with an alternative format, there will be multiple identity blocks. The tools that identified the format will be nested within the identity elements. If multiple tools disagree on a format identity or other metadata values, a status attribute is added to the element with a value of “CONFLICT”. If only a single tool reports a format identity or other metadata value, a status attribute is added to the element with a value of “SINGLE_RESULT”. If multiple tools agree on an identity or value, and none disagree, the status attribute is omitted. A “PARTIAL” value is written when the format can only be partially identified, for example a format name is identified but not a MIME media type. |
Example 1: Successful format identification
In this example, two tools (Jhove 1.5 and file utility 5.04) identified the format as Plain text with a MIME media type of text/plain.
<identification>
<identity format="Plain text" mimetype="text/plain" toolname="FITS" toolversion="0.8.x">
<tool toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.5" />
<tool toolname="file utility" toolversion="5.04" />
</identity>
</identification>
Example 2: Format conflict
In this example, there is a “format conflict”. The tool Exiftool 9.13 identified the format as PCD with MIME media type image/x-photo-cd, but the tool Tika 1.3 identified the format as MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3. Notice in this case that the identification element will carry an attribute status value of CONFLICT.
<identification status="CONFLICT">
<identity format="PCD" mimetype="image/x-photo-cd" toolname="FITS" toolversion="0.8.x">
<tool toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="9.13" />
</identity>
<identity format="MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3" mimetype="audio/mpeg" toolname="FITS" toolversion="0.8.x">
<tool toolname="Tika" toolversion="1.3" />
</identity>
</identification>
2.0 fileInfo
| Semantic unit | 2.0 fileInfo |
| Semantic components | 2.01filepath 2.02filename 2.03size 2.04md5checksum 2.05lastmodified 2.06fslastmodified 2.07created 2.08creatingApplicationName 2.09creatingApplicationversion 2.10inhibitorType 2.11rightsBasis 2.12copyrightBasis 2.13copyrightNote 2.14creatingos |
| Definition | This section contains basic technical metadata not specific to any format |
| Rationale | Each file processed with FITS should have unique file properties to support use and rendering. |
| Data constraint | Container |
| Repeatability | Repeatable |
| Obligation | Automatic |
| Usage notes | Each of the above elements will carry toolname and toolversion attributes to record the name of the tool that is the source of the information. In most cases there will also be a status attribute value equal to SINGLE_RESULT which means that there wasn’t any conflicting information output by a tool. In some cases, for example if tools reported different file creation dates there will be a status value of CONFLICT. |
Example
<fileinfo>
<size toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1">43152124</size>
<creatingApplicationName toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="11.54" status="SINGLE_RESULT">Adobe Photoshop CS6 (Windows)</creatingApplicationName>
<lastmodified toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="11.54" status="CONFLICT">2013:12:16 13:24:36</lastmodified>
<lastmodified toolname="Tika" toolversion="1.21" status="CONFLICT">2013-12-16T07:24:36</lastmodified>
<created toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="11.54" status="SINGLE_RESULT">2013:12:16 13:23:37-06:00</created>
<filepath toolname="OIS File Information" toolversion="1.0" status="SINGLE_RESULT">/Users/UserID/Desktop/Sample_0001.tif</filepath>
<filename toolname="OIS File Information" toolversion="1.0" status="SINGLE_RESULT">0010_Adams_0001-006-1857-02-21_001.tif</filename>
<md5checksum toolname="OIS File Information" toolversion="1.0" status="SINGLE_RESULT">0c8c66bcc9614cd280f44a0ab8181811</md5checksum>
<fslastmodified toolname="OIS File Information" toolversion="1.0" status="SINGLE_RESULT">1387221878000</fslastmodified>
</fileinfo>
3.0 fileStatus
| Semantic unit | 3.0 fileStatus |
| Semantic components | 3.01messageElements 3.01.1well-formed 3.01.2valid 3.01.3message |
| Definition | This section contains validity information if the tools are able to identify a valid format. |
| Rationale | Each file processed with FITS should have a declaration of validity. |
| Data constraint | Container |
| Repeatability | Not repeatable |
| Obligation | Automatic |
| Usage notes | Well-formed and valid elements will indicate a boolean value (true or false) depending on the validation status of the file. |
Example
<filestatus>
<well-formed toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1" status="SINGLE_RESULT">true</well-formed>
<valid toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1" status="SINGLE_RESULT">true</valid>
</filestatus>
4.0 metadata
| Semantic unit | 4.0 metadata |
| Semantic components | 4.01Audio 4.02Document 4.03Image 4.04Text 4.05Video 4.06Container |
| Definition | This section contains the format-specific technical metadata after normalization and consolidation of each tool’s raw output. |
| Rationale | Each file processed with FITS should have unique technical properties to support use and rendering. |
| Data constraint | Container |
| Repeatability | Not repeatable |
| Obligation | Automatic |
| Usage notes | The elements in this section differ depending on the type of the file format (audio, document, image, text, video). Each type-specific section lists the potential elements that can appear. The actual elements depend on what the tools are able to determine for the file. |
Example
<image>
<byteOrder toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1" status="SINGLE_RESULT">little endian</byteOrder>
<compressionScheme toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1">Uncompressed</compressionScheme>
<imageWidth toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1">2982</imageWidth>
<imageHeight toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1">4821</imageHeight>
<colorSpace toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1">RGB</colorSpace>
<referenceBlackWhite toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1" status="SINGLE_RESULT">0 255 0 255 0 255</referenceBlackWhite>
<iccProfileName toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1">EPSON Standard RGB - Gamma 1.8</iccProfileName>
<orientation toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1">normal*</orientation>
<samplingFrequencyUnit toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1">in.</samplingFrequencyUnit>
<xSamplingFrequency toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1">600</xSamplingFrequency>
<ySamplingFrequency toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1">600</ySamplingFrequency>
<bitsPerSample toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1">8 8 8</bitsPerSample>
<samplesPerPixel toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1">3</samplesPerPixel>
<scanningSoftwareName toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.20.1">Adobe Photoshop CS6 (Windows)</scanningSoftwareName>
<iccProfileVersion toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="11.54" status="SINGLE_RESULT">2.2.0</iccProfileVersion>
</image>
4.01 Audio elements
| Semantic unit | 4.01 Audio elements |
| Semantic components | See dropdown below table for list of components |
| Definition | This section contains technical metadata for audio files. The tools will extract the raw output of the file, and FITS normalizes and consolidates the output into the standard elements. |
| Rationale | Each file processed with FITS should have unique technical properties to support use and rendering. |
| Data constraint | Container |
| Repeatability | Not repeatable |
| Obligation | Automatic |
| Usage notes | The list of audio elements represents the potential properties of a given file. The actual elements depend on what the tools are able to determine for the file. |
| Metadata standard | AES standard for audio metadata – Audio object structures for preservation and restoration |
| Short name | AES Audio Object |
| Maintenance organization | Audio Engineering Society, Inc. (AES) |
| Website | http://www.aes.org/standards/blog/2011/9/aes57-2011-metadata-audio-object |
4.01 Audio semantic components
- 4.01.01
- audioDataEncoding
- 4.01.02
- avgBitRate
- 4.01.03
- avgPacketSize
- 4.01.04
- bitDepth
- 4.01.05
- bitRate
- 4.01.06
- blockAlign
- 4.01.07
- blockSizeMax
- 4.01.08
- blockSizeMin
- 4.01.09
- byteOrder
- 4.01.10
- channels
- 4.01.11
- duration
- 4.01.12
- maxBitRate
- 4.01.13
- maxPacketSize
- 4.01.14
- numPackets
- 4.01.15
- numSamples
- 4.01.16
- offset
- 4.01.17
- sampleRate
- 4.01.18
- software
- 4.01.19
- soundField
- 4.01.20
- time
- 4.01.21
- wordSize
Example
<metadata>
<audio>
<numSamples toolname="OIS Audio Information" toolversion="0.1" status="SINGLE_RESULT">299159</numSamples>
<sampleRate toolname="OIS Audio Information" toolversion="0.1">96000</sampleRate>
<audioDataEncoding toolname="OIS Audio Information" toolversion="0.1" status="CONFLICT">PCM</audioDataEncoding>
<audioDataEncoding toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.16" status="CONFLICT">PCM audio in integer format</audioDataEncoding>
<audioDataEncoding toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="10.00" status="CONFLICT">Microsoft PCM</audioDataEncoding>
<blockAlign toolname="OIS Audio Information" toolversion="0.1" status="SINGLE_RESULT">3</blockAlign>
<time toolname="OIS Audio Information" toolversion="0.1" status="SINGLE_RESULT">458028579</time>
<channels toolname="OIS Audio Information" toolversion="0.1">1</channels>
<bitDepth toolname="OIS Audio Information" toolversion="0.1">24</bitDepth>
<wordSize toolname="OIS Audio Information" toolversion="0.1" status="SINGLE_RESULT">3</wordSize>
<offset toolname="OIS Audio Information" toolversion="0.1">46</offset>
<byteOrder toolname="Jhove" toolversion="1.16" status="SINGLE_RESULT">LITTLE_ENDIAN</byteOrder>
<duration toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="10.00" status="SINGLE_RESULT">3.12 s</duration>
</audio>
</metadata>
4.02 Document elements
| Semantic unit | 4.02 Document elements |
| Semantic components | See dropdown below table for list of components |
| Definition | This section contains technical metadata for document files. The tools will extract the raw output of the file, and FITS normalizes and consolidates the output into the standard elements. |
| Rationale | Each file processed with FITS should have unique technical properties to support use and rendering. |
| Data constraint | Container |
| Repeatability | Not repeatable |
| Obligation | Automatic |
| Usage notes | The list of document elements represents the potential properties of a given file. The actual elements depend on what the tools are able to determine for the file. |
| Metadata standard | Document Metadata - document technical metadata for digital preservation |
| Short name | DocumentMD |
| Maintenance organization | Florida Virtual Campus and Harvard Library |
| Website | http://www.fcla.edu/dls/md/docmd |
4.02 Document semantic components
- 4.02.01
- author
- 4.02.02
- hasAnnotations
- 4.02.03
- hasOutline
- 4.02.04
- isProtected
- 4.02.05
- isRightsManaged
- 4.02.06
- isTagged
- 4.02.07
- language
- 4.02.08
- pageCount
- 4.02.09
- title
Example
<metadata>
<document>
<pageCount toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="10.00" status="SINGLE_RESULT">2</pageCount>
<wordCount toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="10.00" status="SINGLE_RESULT">141</wordCount>
<characterCount toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="10.00" status="SINGLE_RESULT">805</characterCount>
<author toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="10.00" status="SINGLE_RESULT">Zakuta, Vitaly</author>
<lineCount toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="10.00" status="SINGLE_RESULT">6</lineCount>
<paragraphCount toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="10.00" status="SINGLE_RESULT">1</paragraphCount>
<standard>
<docmd:document xmlns:docmd="http://www.fcla.edu/docmd">
<docmd:PageCount>2</docmd:PageCount>
<docmd:WordCount>141</docmd:WordCount>
<docmd:CharacterCount>805</docmd:CharacterCount>
<docmd:ParagraphCount>1</docmd:ParagraphCount>
<docmd:LineCount>6</docmd:LineCount>
</docmd:document>
</standard>
</document>
</metadata>
4.03 Image elements
| Semantic unit | 4.03 Image elements |
| Semantic components | See dropdown below table for list of components |
| Definition | This section contains technical metadata for image files. The tools will extract the raw output of the file, and FITS normalizes and consolidates the output into the standard elements. |
| Rationale | Each file processed with FITS should have unique technical properties to support use and rendering. |
| Data constraint | Container |
| Repeatability | Repeatable |
| Obligation | Automatic |
| Usage notes | The list of image elements represents the potential properties of a given file. The actual elements depend on what the tools are able to determine for the file. |
| Metadata standard | NISO Metadata for Images in XML Schema |
| Short name | MIX |
| Maintenance organization | Library of Congress (for NISO) |
| Website | http://www.loc.gov/standards/mix/ |
4.03 Image semantic components
- 4.03.01
- apertureValue
- 4.03.02
- bitsPerSample
- 4.03.03
- brightnessValue
- 4.03.04
- byteOrder
- 4.03.05
- captureDevice
- 4.03.06
- cfaPattern
- 4.03.07
- cfaPattern2
- 4.03.08
- colorMap
- 4.03.09
- colorSpace
- 4.03.10
- compressionScheme
- 4.03.11
- digitalCameraManufacturer
- 4.03.12
- digitalCameraModelName
- 4.03.13
- digitalCameraSerialNo
- 4.03.14
- exifVersion
- 4.03.15
- exposureBiasValue
- 4.03.16
- exposureIndex
- 4.03.17
- exposureProgram
- 4.03.18
- exposureTime
- 4.03.19
- extraSamples
- 4.03.20
- flash
- 4.03.21
- flashEnergy
- 4.03.22
- fNumber
- 4.03.23
- focalLength
- 4.03.24
- gpsAltitudeRef
- 4.03.25
- gpsAltitude
- 4.03.26
- gpsAreaInformation
- 4.03.27
- gpsDateStamp
- 4.03.28
- gpsDestBearing
- 4.03.29
- gpsDestBearingRef
- 4.03.30
- gpsDestDistance
- 4.03.31
- gpsDestDistanceRef
- 4.03.32
- gpsDestLatitude
- 4.03.33
- gpsDestLatitudeRef
- 4.03.34
- gpsDestLongitude
- 4.03.35
- gpsDestLongitudeRef
- 4.03.36
- gpsDifferential
- 4.03.37
- gpsDOP
- 4.03.38
- gpsImgDirection
- 4.03.39
- gpsImgDirectionRef
- 4.03.40
- gpsLatitude
- 4.03.41
- gpsLatitudeRef
- 4.03.42
- gpsLongitude
- 4.03.43
- gpsLongitudeRef
- 4.03.44
- gpsMapDatum
- 4.03.45
- gpsMeasureMode
- 4.03.46
- gpsProcessingMethod
- 4.03.47
- gpsSatellites
- 4.03.48
- gpsSpeed
- 4.03.49
- gpsSpeedRef
- 4.03.50
- gpsStatus
- 4.03.51
- gpsTimeStamp
- 4.03.52
- gpsTrack
- 4.03.53
- gpsTrackRef
- 4.03.54
- gpsVersionID
- 4.03.55
- grayResponseUnit
- 4.03.56
- iccProfileName
- 4.03.57
- iccProfileVersion
- 4.03.58
- imageHeight
- 4.03.59
- imageProducer
- 4.03.60
- imageWidth
- 4.03.61
- isoSpeedRating
- 4.03.62
- lightSource
- 4.03.63
- maxApertureValue
- 4.03.64
- meteringMode
- 4.03.65
- oECF
- 4.03.66
- orientation
- 4.03.67
- primaryChromaticitiesBlueX
- 4.03.68
- primaryChromaticitiesBlueY
- 4.03.69
- primaryChromaticitiesGreenX
- 4.03.70
- primaryChromaticitiesGreenY
- 4.03.71
- primaryChromaticitiesRedX
- 4.03.72
- primaryChromaticitiesRedY
- 4.03.73
- qualityLayers
- 4.03.74
- referenceBlackWhite
- 4.03.75
- resolutionLevels
- 4.03.76
- samplesPerPixel
- 4.03.77
- samplingFrequencyUnit
- 4.03.78
- scannerManufacturer
- 4.03.79
- scannerModelName
- 4.03.80
- scannerModelNumber
- 4.03.81
- scannerModelSerialNo
- 4.03.82
- scanningSoftwareName
- 4.03.83
- scanningSoftwareVersionNo
- 4.03.84
- sensingMethod
- 4.03.85
- shutterSpeedValue
- 4.03.86
- spectralSensitivity
- 4.03.87
- subjectDistance
- 4.03.88
- tileHeight
- 4.03.89
- tileWidth
- 4.03.90
- whitePointXValue
- 4.03.91
- whitePointYValue
- 4.03.92
- xSamplingFrequency
- 4.03.93
- ySamplingFrequency
- 4.03.94
- YCbCrCoefficients
- 4.03.95
- YCbCrPositioning
- 4.03.96
- YCbCrSubSampling
4.04 Text elements
| Semantic unit | 4.04 Text elements |
| Semantic components | See dropdown below table for list of components |
| Definition | This section contains technical metadata for text files. The tools will extract the raw output of the file, and FITS normalizes and consolidates the output into the standard elements. |
| Rationale | Each file processed with FITS should have unique technical properties to support use and rendering. |
| Data constraint | Container |
| Repeatability | Repeatable |
| Obligation | Automatic |
| Usage notes | The list of text elements represents the potential properties of a given file. The actual elements depend on what the tools are able to determine for the file. |
| Metadata standard | Technical Metadata for Text |
| Short name | TextMD |
| Maintenance organization | Library of Congress |
| Website | http://www.loc.gov/standards/textMD/ |
4.04 Text semantic components
- 4.04.01
- charset
- 4.04.02
- linebreak
- 4.04.03
- markupBasis
- 4.04.04
- markupBasisVersion
- 4.04.05
- markupLanguage
Example
<metadata>
<text>
<charset toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="12.29" status="SINGLE_RESULT">us-ascii</charset>
<linebreak toolname="Exiftool" toolversion="12.29" status="SINGLE_RESULT">CR</linebreak>
<standard>
<textMD:textMD xmlns:textMD="info:lc/xmlns/textMD-v3">
<textMD:character_info>
<textMD:charset>US-ASCII</textMD:charset>
<textMD:linebreak>CR</textMD:linebreak>
</textMD:character_info>
</textMD:textMD>
</standard>
</text>
</metadata>
4.05 Video elements
| Semantic unit | 4.05 Video elements |
| Semantic components | See dropdown below table for list of components |
| Definition | This section contains technical metadata for image files. The tools will extract the raw output of the file, and FITS normalizes and consolidates the output into the standard elements. |
| Rationale | Each file processed with FITS should have unique technical properties to support use and rendering. |
| Data constraint | Container |
| Repeatability | Repeatable |
| Obligation | Automatic |
| Usage notes | The list of video elements represents the potential properties of a given file. The actual elements depend on what the tools are able to determine for the file. |
| Metadata standard | EBUCore metadata |
| Short name | EBUCore |
| Maintenance organization | European Broadcasting Union |
| Website | https://tech.ebu.ch/MetadataEbuCore |
4.05 Video semantic components
- 4.05.01
- apertureSetting
- 4.05.02
- bitDepth
- 4.05.03
- bitRate
- 4.05.04
- blockSizeMax
- 4.05.05
- blockSizeMin
- 4.05.06
- channels
- 4.05.07
- creatingApplicationName
- 4.05.08
- dataFormatType
- 4.05.09
- digitalCameraManufacturer
- 4.05.10
- digitalCameraModelName
- 4.05.11
- duration
- 4.05.12
- exposureTime
- 4.05.13
- exposureProgram
- 4.05.14
- fNumber
- 4.05.15
- focus
- 4.05.16
- frameRate
- 4.05.17
- gain
- 4.05.18
- gpsAltitude
- 4.05.19
- gpsAltitudeRef
- 4.05.20
- gpsAreaInformation
- 4.05.21
- gpsDateStamp
- 4.05.22
- gpsDestBearing
- 4.05.23
- gpsDestBearingRef
- 4.05.24
- gpsDestDistance
- 4.05.25
- gpsDestDistanceRef
- 4.05.26
- gpsDestLatitude
- 4.05.27
- gpsDestLatitudeRef
- 4.05.28
- gpsDestLongitude
- 4.05.29
- gpsDestLongitudeRef
- 4.05.30
- gpsDifferential
- 4.05.31
- gpsDOP
- 4.05.32
- gpsImgDirection
- 4.05.33
- gpsImgDirectionRef
- 4.05.34
- gpsLatitude
- 4.05.35
- gpsLatitudeRef
- 4.05.36
- gpsLongitude
- 4.05.37
- gpsLongitudeRef
- 4.05.38
- gpsMapDatum
- 4.05.39
- gpsMeasureMode
- 4.05.40
- gpsProcessingMethod
- 4.05.41
- gpsSatellites
- 4.05.42
- gpsSpeed
- 4.05.43
- gpsSpeedRef
- 4.05.44
- gpsStatus
- 4.05.45
- gpsTimeStamp
- 4.05.46
- gpsTrack
- 4.05.47
- gpsTrackRef
- 4.05.48
- gpsVersionID
- 4.05.49
- imageHeight
- 4.05.50
- imageStabilization
- 4.05.51
- imageWidth
- 4.05.52
- sampleRate
- 4.05.53
- shutterSpeedValue
- 4.05.54
- videoStreamType
- 4.05.55
- whiteBalance
- 4.05.56
- xSamplingFrequency
- 4.05.57
- ySamplingFrequency
Example
<metadata>
<video>
<location toolname="MediaInfo" toolversion="0.7.75" status="SINGLE_RESULT">/Users/dan179/git/git-daveneiman/fits/testfiles/FITS-SAMPLE-44_1_1_4_4_4_6_1_1_2_3_1.mp4</location>
<mimeType toolname="MediaInfo" toolversion="0.7.75" status="SINGLE_RESULT">video/quicktime</mimeType>
<format toolname="MediaInfo" toolversion="0.7.75" status="SINGLE_RESULT">MPEG-4</format>
<formatProfile toolname="MediaInfo" toolversion="0.7.75" status="SINGLE_RESULT">Base Media / Version 2</formatProfile>
<duration toolname="MediaInfo" toolversion="0.7.75" status="SINGLE_RESULT">4137</duration>
<bitRate toolname="MediaInfo" toolversion="0.7.75" status="SINGLE_RESULT">17585272</bitRate>
<dateCreated toolname="MediaInfo" toolversion="0.7.75" status="SINGLE_RESULT">UTC 2015-03-13 19:21:21</dateCreated>
<dateModified toolname="MediaInfo" toolversion="0.7.75" status="SINGLE_RESULT">UTC 2015-11-04 22:09:23</dateModified>
<track type="video" id="1" toolname="MediaInfo" toolversion="0.7.75" status="SINGLE_RESULT">
<videoDataEncoding>avc1</videoDataEncoding>
<codecId>avc1</codecId>
<codecCC>avc1</codecCC>
<codecVersion>Main@L4.1</codecVersion>
<codecName>AVC</codecName>
<codecFamily>H.264</codecFamily>
<codecInfo>Advanced Video Codec</codecInfo>
<compression>Unknown</compression>
<byteOrder>Unknown</byteOrder>
<bitDepth>8 bits</bitDepth>
<bitRate>17375067</bitRate>
<duration>4137</duration>
<trackSize>8986104</trackSize>
<width>1440 pixels</width>
<height>1080 pixels</height>
<frameRate>29.970</frameRate>
<frameRateMode>Constant</frameRateMode>
<frameCount>124</frameCount>
<aspectRatio>4:3</aspectRatio>
<scanningFormat>Interlaced</scanningFormat>
<scanningOrder>TFF</scanningOrder>
<chromaSubsampling>4:2:0</chromaSubsampling>
<colorspace>YUV</colorspace>
<broadcastStandard>NTSC</broadcastStandard>
</track>
<track type="audio" id="2" toolname="MediaInfo" toolversion="0.7.75" status="SINGLE_RESULT">
<audioDataEncoding>AAC</audioDataEncoding>
<codecId>40</codecId>
<codecFamily>AAC</codecFamily>
<compression>Lossy</compression>
<bitRate>228374</bitRate>
<bitRateMode>Variable</bitRateMode>
<duration>4137</duration>
<trackSize>97970</trackSize>
<soundField>Front: L R</soundField>
<samplingRate>48000</samplingRate>
<numSamples>198576</numSamples>
<channels>2</channels>
</track>
</video>
</metadata>
4.06 Container elements
| Semantic unit | 4.06 Container elements |
| Semantic components | N/A |
| Definition | This section identifies the standard used to wrap file-specific sections. |
| Rationale | The container element can extend established schemas or wrap the output of a characterization tool. |
| Data constraint | Container |
| Repeatability | Repeatable |
| Obligation | Automatic |
| Usage notes | The containerMD standard contains a description of the container and two levels of verbosity. it can be used to extend certain container formats, and the container element can include format-specific technical metadata. |
| Metadata standard | ContainerMD |
| Short name | ContainerMD |
| Maintenance organization | Bibliothèque Nationale de France |
| Website | http://bibnum.bnf.fr/containerMD-v1_1/index.html |
Example
<metadata>
<container>
<originalSize toolname="Droid" toolversion="6.4" status="SINGLE_RESULT">34318329</originalSize>
<compressionMethod toolname="Droid" toolversion="6.4" status="SINGLE_RESULT">deflate</compressionMethod>
<entries totalEntries="17" toolname="Droid" toolversion="6.4" status="SINGLE_RESULT">
<format name="EPUB" number="1" />
<format name="Extensible Markup Language" number="1" />
<format name="Graphics Interchange Format" number="1" />
<format name="JPEG 2000 JP2" number="1" />
<format name="JPEG File Interchange Format" number="1" />
<format name="MPEG-4" number="1" />
<format name="Office Open XML Document" number="1" />
<format name="OpenDocument Text" number="1" />
<format name="PDF/A" number="1" />
<format name="PDF/X" number="1" />
<format name="Plain text" number="1" />
<format name="Portable Network Graphics" number="1" />
<format name="Rich Text Format (RTF)" number="1" />
<format name="TIFF EXIF" number="1" />
<format name="Waveform Audio" number="2" />
<format name="ZIP Format" number="1" />
</entries>
</container>
</metadata>
FITS configuration files
The FITS configuration files are located in the xml directory.
The FITS XML output is highly affected by how FITS is configured. In particular, the order of tools near the top of the fits.xml configuration file specifies which tools FITS should prefer when they give conflicting information and if FITS should ignore tool output for particular formats. FITS comes pre-configured based on testing different tools with different formats and the default configuration should only be changed with a great deal of care and testing.
fits.xml
This is the main configuration file for FITS. The key pieces are described here:
tool element
Lists all the tools that FITS should know about. The order of these elements determines the preference in favoring one tool over another, for example when there are multiple tools reporting formats or technical metadata for a file.
The following are attributes of the tool element:
- class (required) - specifies the fully qualified name of the Java class that implements the Tool interface
- exclude-exts (optional) - specifies by file extension files that the tool should not process. This is useful if you know a tool misidentifies or generates inaccurate metadata for specific types of files
- include-exts (optional) - indicates to FITS to use the information reported by the tool for particular file extensions
- classpath-dirs (optional) - for Java-based tools when there is a need to provide class isolation via a custom class loader. By convention, any tool-specific JAR files, including any 3rd-party dependencies, should be put into a
lib/<tool-name>directory. Additional directories can be added for configuration files that need to be discovered via the tool’s class loader. These files might go in, for example,xml/<tool-name>. This custom class loader will load classes from the bottom up (rather than the standard Java top down scheme). The value for this attribute is the name of the sub-directory containing any JAR files for this tool.
output element
Contains elements that control FITS metadata output:
- data-consolidator - specifies the class to use for consolidating the tool output. It’s possible to use custom logic to control the tool output consolidation processes by creating a class implementing the ToolOutputConsolidator interface.
- display-tool-output - whether or not to append the output of the native tool output for each tool to the final consolidated FITS XML output, can be set to either true or false
- report-conflicts - whether or not to report when there is conflicting tool information about formats or metadata, can be set to either true or false. If set to true, conflicts will be shown in the final FITS XML output. If set to false, only the output from the most preferred tool (controlled by the ordering of the tool elements) will be displayed.
- validate-tool-output - whether or not to validate tool output, can be set to either true or false. Generally this should be set to true. Setting it to false will disable schema validation of the output from each tool.
- NOTE: The local copy provided with FITS is used for validation during the file processing. As each tool has its output converted to the FITS format it is validated using the local schema. This can be disabled by setting
<validate-tool-output>in xml/fits.xml to false.
- NOTE: The local copy provided with FITS is used for validation during the file processing. As each tool has its output converted to the FITS format it is validated using the local schema. This can be disabled by setting
- internal-output-schema - the location of the local copy of the XML schema specifying the FITS XML output, used during FITS execution
- external-output-schema - the location of the remote XML schema controlling the FITS XML output, written to the output file
- fits-xml-namespace - the XML namespace to use in the FITS XML output
- enable-statistics - whether or not to output the statistics block containing performance metrics about each tool that processed the file, can be set to either true or false enable-checksum - whether or not to compute the MD5 checksum for the file, can be set to either true or false
- checksum-exclusions - file extensions to be excluded in the checksum calculation.
- NOTE: This configuration parameter will only be enforced if the above enable-checksum is set to true.
process/maxThreads element
The maximum number of threads to use
droid_sigfile element
The signature file to use with the Droid tool. Get the list of all previously released signature files
droid_read_limit element
This allows for limiting the amount of a file (from its beginning) that is to be examined by the DROID tool (in order to increase processing speed). For example, for some types of large video and audio files, only the first 64K bytes need to be examined to extract relevant metadata. The attribute include-exts sets the file extension that this limiter should be applied to, and the attribute read-limit-kb sets the limit, in kilobytes, of how much of the beginning of the designated file types should be examined. The default behavior (when this element remains commented-out) is for DROID to examine all files in their entirety.
fits_format_tree.xml
Certain formats are a more specific subset of a more general format. The format tree in this file specifies these relationships. Nested formats are more specific versions of the formats they are nested under. FITS uses this to know when to report format conflicts and when it should report a more specific format.
During output consolidation the format tree is consulted, and any less specific format identities are thrown out. For example, OpenOffice text document formats are ZIP-based. Some tools identify these files as ZIP, and others as ODT. Any tools identifying the file as a ZIP would be discarded according to the rules set by the format tree.
An example follows using a snippet of the format tree:
<branch format="JPEG 2000">
<branch format="JPEG 2000 JP2" />
<branch format="JPEG 2000 JPX" />
</branch>
The above snippet of the format tree should be interpreted as: JPEG 2000 JP2 and JPEG 2000 JPX are more specific forms of the JPEG 2000 format. If one FITS-wrapped tool were to report the format of a file as JPEG 2000 and another reported it as JPEG 2000 JP2, FITS would report the more specific format (JPEG 2000 JP2) and would not report that there was a format conflict (because both tools were technically correct).
fits_output.xsd
Schema for the output of FITS XML files.
fits_xml_map.xml
This mapping file is used to normalize the values output by some of the tools that FITS wraps, for example to change Jhove’s Greyscale value to Grayscale. It allows substitution of one value for another on a tool by tool, element by element basis.
For example, if a tool outputs the value “2” as the sampling frequency unit for an image, but you want to use the text string “inches” instead, you could add an entry to fits_xml_map.xml. Mappings are applied automatically when a tool creates its FITS output, prior to output consolidation. You must specify the tool name, version, and element name that you want mapped. Currently all mapping-related needs are handled in the tool’s XSLT.
format_map.txt
The file is used to normalize format names output by some of the tools that FITS wraps.
mime_map.txt
The file is used to normalize MIME media type values output by some of the tools that FITS wraps.
mime_to_format_map.txt
Used to map format names to MIME media types for some of the tools that FITS wraps.
prettyprint.xslt
Transforms the standard FITS output into “pretty print” XML formatting for easier human readability.
xslt_map.xsd
Schema for transformation maps for these tools: exiftool_xslt_map.xml, jhove_xslt_map.xml, nlnx_xslt_map.xml.
Tools & Libraries
The latest version of FITS is configured to a number of open source projects. All project licenses are available in our GitHub repository.
ADL Tool
| Maintenance organization | Harvard Library |
| Capabilities | Identifies and extracts edit decision lists from audio files. |
| Formats supported | Audio Decision List files |
| Description | The ADL tool acts on ADL files and applies the Audio Engineering Society (AES) standard for transfer and exchange of edit data. |
| Usage notes | Audio Decision List files support interchange of audio files and projects and the ADL Tool extracts this data from audio files. |
Apache Tika
| Maintenance organization | Apache |
| Capabilities | Identifies file formats |
| Formats supported | See full list of supported formats |
| Description | Tika extracts text and metadata from hundreds of file formats. |
| Usage notes | While Tika can parse hundreds of formats, FITS uses Tika primarily to extract technical metadata from document-type files. |
DROID
| Maintenance organization | UK National Archives |
| Capabilities | Profiles a range of file formats and identifies version, age, size, and date of last modification. |
| Formats supported | Supports over 1,000 formats, which are listed in the DROID signature file |
| Description | The core function of DROID is accurate file format identification, even if the files are missing extensions or if they are in a container file. DROID is written in Java. |
| Usage notes | The FITS tool wrapper uses the provided API. The output is converted into a simple XML document and then converted to FITS XML using xml/droid/droid_to_fits.xslt. The DROID configuration file and signature file are located in the tools/droid directory. |
embARC
| Maintenance organization | Library of Congress |
| Capabilities | Identify and extract complete metadata from SMPTE DPX image files. |
| Formats supported | dpx |
| Description | embARC is written in Java. The FITS tool wrapper uses the provided API. Raw tool output is provided in XML format. |
| Usage notes | Although the standalone embARC application processes DPX sequences natively, this integration with FITS only supports the processing of DPX files individually and not as a sequence. |
ExifTool
| Maintenance organization | Phil Harvey |
| Capabilities | Identifies and extracts technical metadata. |
| Formats supported | jpg, tiff, jp2, gif, bmp, png, psd, dng, wav, mp3, mp4, m4a, aiff, rm, ogg, flac, xml, html, pdf, doc |
| Description | Exiftool is written in Perl. A windows executable is also provided. The Exiftool tool wrapper detects the operating system type and calls the appropriate version of the tool. |
| Usage notes | The tab-delimited output is captured, converted to a simple XML structure, and then converted to FITS XML using xslt. xml/exiftool/exiftool_xslt_map.xml is used to determine which XSLT to apply for the given identified format. |
ffident (archived site)
| Maintenance organization | no longer maintained |
| Capabilities | Identifies file formats. |
| Formats supported | Listed in the configuration file tools/ffident/formats.txt |
| Description | FFIdent is written in Java. |
| Usage notes | The FITS tool wrapper uses the provided API. Output is converted into a simple XML document and then converted to FITS XML using xml/ffident/ffident_to_fits.xslt. |
File utility (windows port)
| Maintenance organization | GnuWin project |
| Capabilities | Identifies files. |
| Formats supported | many (> 1,000) |
| Description | File Utility is a package that is usually bundled with Linux, UNIX and OS X. The GnuWin32? port is provided for use on Windows. Due to variations in versions this may cause different output when run on different platforms. File Utility is called in its default mode (no arguments), and also with -i to determine the MIME type. |
| Usage notes | The output is converted into a simple XML document and then converted to FITS XML using xml/fileutility/fileutility_to_fits.xslt |
Jhove
| Maintenance organization | Open Preservation Foundation |
| Capabilities | Identifies, extracts technical metadata, and validates files. |
| Formats supported | jpg, tiff, jp2, gif, wave, aiff, xml, html, ascii, utf-8, pdf |
| Description | JHOVE is a software framework for format identification, validation, and characterization of digital objects. JHOVE is written in Java. JHOVE does not validate the codestream but it checks the file structure. |
| Usage notes | The FITS tool wrapper uses the provided API. The JHOVE XML output is converted to FITS XML using XSLT. xml/jhove/jhove_xslt_map.xml is used to determine which XSLT to apply for the given identified format. Note - For JP2 files the JHOVE output element Transformation indicates whether the compression is lossy or lossless. The transformation values are described in Table A-20 of the JPEG2000 part 1 specification. A value of 0 maps to the 9-7 irreversible (lossy) filter. A value of 1 maps to 5-3 reversible (lossless) filter. This JHOVE element is used by FITS when it outputs the compressionScheme in the image metadata, writing it as JPEG 2000 Lossy or JPEG 2000 Lossless. |
MediaInfo
| Maintenance organization | MediaArea.net |
| Capabilities | Identifies and extracts technical metadata for video files. |
| Formats supported | Although MediaInfo supports many video formats, FITS will only support the following video formats and wrappers out of the box - avi, mov, mpg, mpeg, mkv, mp4, mxf, ogv, mj2, divx, dv, m4v, m2v, ism. |
| Description | The MediaInfo API is written in C++ and is called via Java by using the JNA library. |
| Usage notes | The FITS tool wrapper uses the MediaInfo API. The MediaInfo XML output is converted to FITS XML using XSLT. |
Metadata Extractor Tool
| Maintenance organization | National Library of New Zealand |
| Capabilities | Identifies and extracts technical metadata. |
| Formats supported | jpg, tiff, gif, bmp, wav, mp3, xml, html, pdf, doc, wordperfect, msworks, odt |
| Description | The FITS NLNZ tool wrapper uses the provided Java API. |
| Usage notes | The NLNZ native XML output is converted to FITS XML using XSLT. xml/nlnz/fits/nlnz_xslt_map.xml is used to determine which XSLT to apply to the given identified format. |
OIS Audio Information
| Maintenance organization | Harvard Library |
| Capabilities | Identifies and extracts technical metadata |
| Formats supported | audio |
| Description | The OIS Audio Information tool identifies audio formats and applies AES metadata standards to extracted technical metadata. |
| Usage notes | OIS Audio Information creates FITS XML without further normalization. |
OIS File Information
| Maintenance organization | Harvard Library |
| Capabilities | Extracts technical metadata. |
| Formats supported | any |
| Description | FileInfo creates FITS XML without further normalization. It determines basic file information like file name, size, file system last modified date, and md5 checksums. It uses the fast md5 jar from http://www.twmacinta.com/myjava/fast_md5.php. |
| Usage notes | OIS FileInfo creates FITS XML without further normalization. |
OIS XML Information
| Maintenance organization | Harvard Library |
| Capabilities | Identifies and extracts technical metadata. |
| Formats supported | XML |
| Description | The OIS XML Information tool identifies XML and parses out the default namespace and schema location. |
| Usage notes | XmlMetadata creates FITS XML without further normalization. Used for FITS text metadata. |
VTT Tool
| Maintenance organization | Harvard Library |
| Capabilities | Extracts and validates VTT video caption files |
| Formats supported | video |
| Description | VTT Tool is written in Java. |
| Usage notes | VTT Tool creates FITS XML without further normalization. |